close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-10 Origin: Site









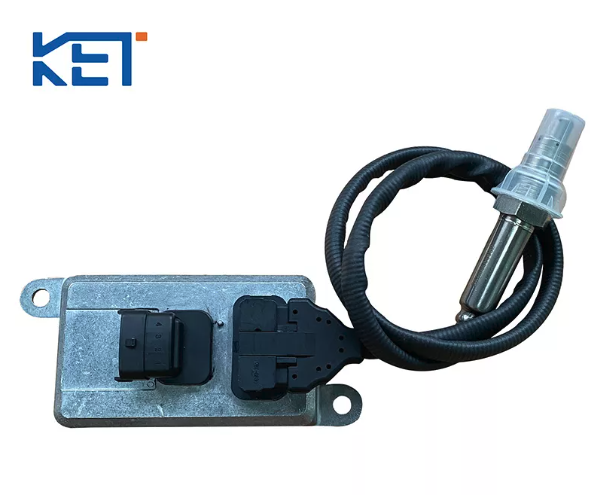
Modern diesel engines rely heavily on precise emission control systems to meet ever-tightening environmental standards. Among these systems, the NOx sensor and the Engine Control Unit (ECU) play crucial roles in ensuring clean, efficient combustion and compliance with emission regulations.
When a NOx sensor fails, it can trigger the Check Engine Light, reduce fuel efficiency, and even cause your vehicle to enter limp mode. Replacing the faulty sensor is only part of the solution — understanding whether or not you need to reset the ECU afterward is equally important.
This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about ECU resets after NOx sensor replacement: why it matters, how to do it properly, and what to expect afterward. Whether you’re a DIY mechanic or a professional technician, these insights will help you maintain optimal engine performance, protect expensive components like the Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) system, and extend the life of your diesel vehicle.
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) is the vehicle’s brain. It collects data from sensors, including NOx, oxygen, temperature, and pressure sensors, then uses that data to manage engine operations.
The ECU relies on NOx sensors to:
Adjust DEF dosing in SCR systems
Optimize fuel injection for clean combustion
Manage turbocharger boost for efficient performance
Control diesel particulate filter (DPF) regeneration cycles
Without accurate NOx readings, the ECU cannot maintain emissions standards or optimal engine performance, which may lead to long-term engine damage.
Knowing when to replace a NOx sensor is critical for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and keeping emissions within legal limits. A NOx sensor plays an essential role in monitoring the concentration of nitrogen oxides in exhaust gases and sending real-time data to the engine control unit (ECU). When this sensor begins to fail, the vehicle’s emission control system can no longer function properly, leading to higher emissions, poor fuel economy, and potential damage to expensive exhaust components.
You might also notice other symptoms such as a reduction in fuel efficiency, erratic idling, or failed emissions testing results. In some cases, the vehicle may enter a limp mode to prevent further engine damage, limiting power and speed.
Even if your vehicle appears to be running smoothly, manufacturers often recommend replacing the NOx sensor at regular intervals—typically every 80,000 to 100,000 miles for diesel engines. Following this schedule helps prevent sudden failures and ensures that the Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) system and Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) function efficiently. Ignoring a failing sensor can result in excessive fuel injection, soot buildup, and even long-term damage to these costly emission components.
Replacing a NOx sensor is not overly complex, but it requires attention to detail and basic mechanical skills. Here’s a detailed walkthrough of the process.
To complete the replacement successfully, you will need a socket and wrench set (usually a 22 mm or 24 mm oxygen sensor socket), an OBD2 diagnostic scanner, and an anti-seize compound to apply to the sensor threads. Safety equipment, including gloves and eye protection, is also important to avoid injury when working under the vehicle or near hot exhaust components.
Most diesel vehicles are equipped with two NOx sensors—one positioned upstream (before the SCR catalyst) and another downstream (after the SCR catalyst). The upstream sensor measures NOx levels leaving the engine, while the downstream sensor monitors the efficiency of the SCR system. Consult your vehicle’s service manual or online diagrams to confirm the exact location.
Before you begin removing the sensor, disconnect the vehicle’s battery. This step prevents accidental short circuits and ensures the ECU resets properly after installation. It’s also a necessary safety precaution to avoid electrical damage to sensitive components.
Locate the sensor wiring harness and disconnect it carefully by pressing the release tab and pulling it free. Avoid tugging directly on the wires. Once disconnected, use the appropriate socket to loosen and unscrew the old sensor from the exhaust pipe. If the sensor is stuck due to rust or heat buildup, apply a penetrating lubricant and allow it to sit for several minutes before trying again.
Before threading in the new sensor, apply a small amount of anti-seize compound to the threads if recommended by the manufacturer. This prevents the sensor from becoming seized in the exhaust over time. Screw in the new sensor by hand first to avoid cross-threading, then tighten it securely using a wrench. Reconnect the wiring harness, ensuring it clicks firmly into place.
Once everything is installed, double-check all electrical connections and wiring harnesses for proper alignment and secure fit. Reconnect the battery and start the engine. Allow the vehicle to idle while monitoring for any warning lights or irregular exhaust behavior.
At this stage, it’s common for the Check Engine Light to remain on until you clear the existing fault codes. Use an OBD2 scanner to erase the NOx-related codes (such as P2201 or P2202). In some vehicles, the ECU may automatically recalibrate after a few drive cycles, but manually clearing the codes ensures a faster reset and prevents false readings.

Failing to reset the ECU after replacing the NOx sensor may cause:
Persistent error codes and the Check Engine Light remaining on.
Delayed adaptation to the new sensor, which can temporarily affect fuel efficiency and emissions.
SCR system may not operate at full efficiency, causing DEF waste or incomplete NOx reduction.
There are several methods to reset your ECU:
Using an OBD2 Scanner:
Connect the scanner, read and clear fault codes.
This ensures the ECU immediately recognizes the new sensor.
Battery Disconnect Method:
Disconnect the negative battery cable for 15–30 minutes.
Resets the ECU, but may also reset radio presets and other stored settings.
Manufacturer-Specific ECU Reset:
Some vehicles require a specific procedure to recalibrate after sensor replacement.
Refer to the vehicle’s service manual or repair guide.
Modern ECUs in some vehicles automatically detect new NOx sensors and recalibrate. However, manually resetting ensures:
Immediate recognition of the new sensor
Clearing of persistent error codes
Optimal SCR system performance
| Method | Procedure | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Using an OBD2 Scanner | Connect the scanner, read and clear fault codes. | Ensures the ECU immediately recognizes the new sensor. |
| Battery Disconnect Method | Disconnect the negative battery cable for 15–30 minutes. | Resets the ECU, but may also reset radio presets and other stored settings. |
| Manufacturer-Specific ECU Reset | Follow the specific procedure for recalibration after sensor replacement. | Refer to the vehicle’s service manual or repair guide. |
Once the new NOx sensor is installed and the ECU has been reset, it’s important to verify that all error codes have been successfully cleared. Start the vehicle and use an OBD2 scanner to confirm that no Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) remain stored in the system. A properly functioning ECU should no longer display any NOx-related codes.
Afterward, monitor the Check Engine Light over several driving cycles — usually two to three complete warm-up and cool-down sessions. This ensures the system has recognized the new sensor and that the ECU is receiving accurate readings. You can also use your diagnostic tool to view live data, confirming that the sensor’s NOx readings are fluctuating as expected during engine operation. Stable and responsive data indicates that the new sensor and ECU communication are functioning properly.
If the Check Engine Light returns or codes persist, this could signal a secondary issue, such as wiring damage, a malfunctioning SCR component, or incomplete ECU adaptation. In that case, further diagnostics will be necessary.
Following NOx sensor replacement, diesel engines may require some time to relearn optimal parameters for the SCR and DPF systems. During this adaptation period, the ECU recalibrates air-fuel ratios, urea injection rates, and exhaust aftertreatment timing.
It’s normal for the vehicle to undergo several regeneration cycles of the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) before performance stabilizes. Drivers may notice smoother acceleration, improved throttle response, and slightly better fuel efficiency after the ECU has fully adapted to the new sensor.
Pay attention to any unusual symptoms during this period, such as engine hesitation, vibrations, or the reappearance of warning lights. These could indicate residual problems or improper installation. In such cases, rechecking all connections and performing another diagnostic scan is advisable.
Replacing a NOx sensor is often within the capabilities of a skilled DIY enthusiast, especially when armed with the right tools and a quality OBD2 scanner. However, professional diagnostics may be necessary in certain situations.
If error codes persist after multiple resets, or the ECU fails to recognize the new sensor despite proper installation, a certified technician can perform advanced testing with manufacturer-specific diagnostic software. Professionals can also run emission system tests to confirm that the vehicle meets regulatory standards, which is especially important before inspections or certifications.
Not necessarily. Some modern ECUs recalibrate automatically, but manual reset ensures proper recognition.
Yes, but old error codes may persist and SCR system performance might be temporarily suboptimal.
It may take a few driving cycles or regeneration events for full adaptation.
Only after resetting the ECU or clearing error codes.
Direct damage is rare, but prolonged operation with a faulty sensor may cause incorrect ECU adjustments, affecting performance.
Replacing a NOx sensor is more than a routine repair — it’s a key step in maintaining your vehicle’s environmental performance and long-term reliability. However, resetting the ECU after installation ensures that the new sensor integrates seamlessly into the engine management system. By clearing old fault codes and allowing the ECU to recalibrate, you’ll restore proper communication between the sensor, SCR system, and DPF, resulting in smoother operation, improved fuel economy, and compliance with emission standards.
If persistent error codes or performance issues remain after replacement, professional diagnostics may be necessary to perform adaptive learning or deeper calibration.
For drivers, repair shops, and distributors seeking high-quality NOx sensors and automotive electronic components, Zhejiang Kreation Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. is your trusted partner. With advanced manufacturing capabilities, strict quality control, and a wide range of emission control solutions.